Stronger, more functional pursuit coreMany lifts and fitness lovers are often amazed. Should I focus more on boards or seats? While two exercises are known, they are actually quite a different approach to basic courses.
Is plank is Isometric development This highlights stability, postal control and muscle endurance.
On the other hand, seat is Dynamic movement It is the abdominal flexion, emphasizing the mobility and contraction force.
Each method has restrictions on its benefits and restrictions, depending on your educational goals, health and general quality of movement. Will study this article Differences between board and seatsApplying to topics such as Basic activationTo be in style Spinal HealthTo be in style Coreand Functional performanceHelping you decide which exercise best suits your daily life.
Basic anatomy. What do we try to strengthen?
The term “CORIN” Includes more than just visible abdominal muscles. The main components of the kernels include:
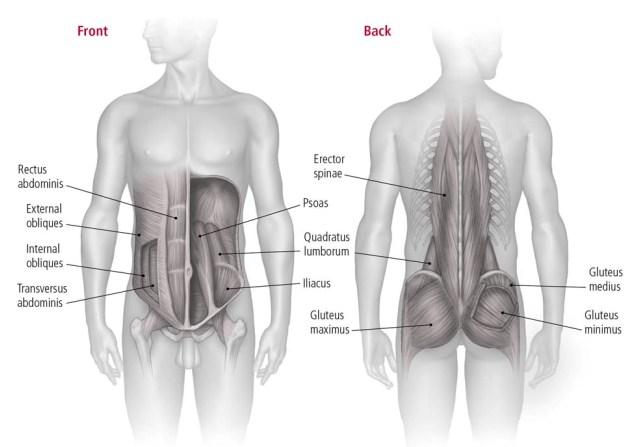
- Recto abdomen – Responsible for long-distance flexibility and is usually activated during a sit-in.
- Transverse abdomen – Deep stabilizer that helps maintain intra-community pressure on boards like flare exercises.
- Internal and external deviations – Help rotation, side flexibility and conflict tasks.
- Erector spines – Stabilizes the spine with an extension.
- Multifunction, pelvic floor and diaphragm – Often neglected, these muscles are necessary for postal management and spinal stabilization.
Effective Basic Course Program must be delivered both movement and stability operates through the forward, backward and side chains.
What is the board?
Eght plank Isometric exercise where you keep a straight, built-in posture, your weight when supporting your forearms and feet. Your spine remains a Neutral positionAnd the muscles of your main environment are involved without any joint movement.
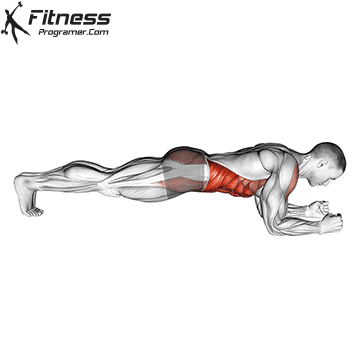
Basic advantages of boards.
- Stimulates Spinal stability and reduces the very big movement of Lumbar.
- Trains: transverse abdomen and the deepest muscles that are difficult to target dynamic exercises.
- Can safely scale with variations (eg side boards, rkc boards, raised boards).
- Offers high The cost of main resistance by compression relatively low spine.
Boards are widely used for recovery, sports courses and general fitness parameters for low risk of injury and versatility.
What is the sit-in?
Is seat A classic trunk is a flexible exercise, where the learner begins with the position of the dwarf and raises the button on his knees. It is mainly targeted Recto abdomen and, to a smaller degree, Hip Flexors: such as iliopsoas and Rectus Femoris.
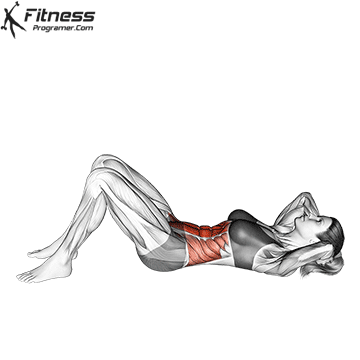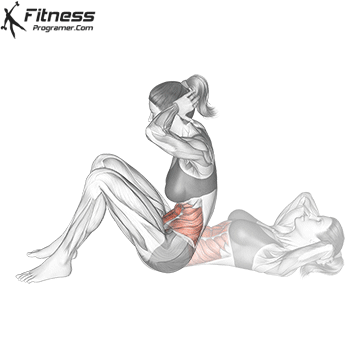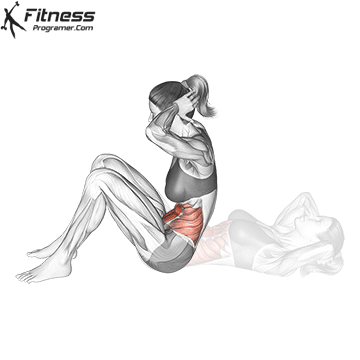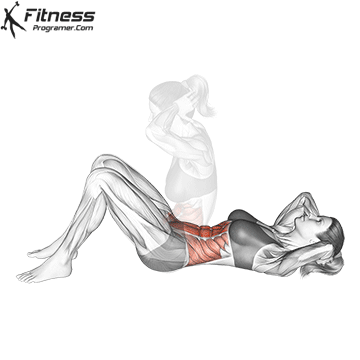
Benefits of sit-offs.
- It builds Dynamic force into the abdominal muscles.
- Encourages Flexibility of active spinewhich can improve mobility when supervised.
- Involves Hip Flexors: and other long-distance flexors, contributing to the general body’s sporting movement.
However, sitters also include Double spine flexibility beneath overloadwhich has aroused concerns about Lumbar disk stress when done inappropriately or excessively.
Comparison of muscle activation
| Exercise | The primary muscles were employed | Type of contraction |
|---|---|---|
| Plank | In the abdominal, rectus abdomen, blades, multifunctional | Isometric (static keeping) |
| Seat | Rectus Abdominis, Hip Flexors, Obliques | Dynamic (concentric / eccentric) |
While two exercises activate the main one: plank Exceed developing Static poster power and a deep basic recruiting, meanwhile seat It focuses more Motion-based force In rectus abdominis.
Risk of spinal health and injury
This is perhaps the most discussed side of the board – a comparison of a sit-in.
- Boards maintain a Neutral spine and are generally considered Spinal Safeespecially for pre-existing back pain or individuals with disk problems.
- Sit-offs, in particular, when being done by anchoring momentaries or feet can grow Lumbar spinal compression and cutting forcesA number of repetitive flexibility, especially in poorly, can increase the risk of disk herdism to be subject to individuals (McGill, 2007).
According to the spinal biology expert Dr. Stuart McGill, the boards are preferable Development of main stability without compromising of spinal healthMeanwhile, sitters can be contraindicated for a particular population.
Main resilience vs. main force. What is your purpose?
- If your goal is to build enduranceStability and postbalial control for sports or longevity activities, boards and their variations are superior.
- If your goal is to develop Strength and power by a dynamic trunk, especially for sports, gymnastics or MMA, such as wrestling, SITINES AND FLEXICE-based exercises can still play a roleIt is provided with the integrity of the spinalA number
A good rounded app can include both but Boards offer more versatile and fewer risks in the total population.
Programming recommendations
For beginners or to those who have a back pain;
- Start with Forearm planksPromotion for longer storage or weighted boards because stability improves.
- Include Side boards aeration of Bird dogs to attract the chain of anti-diaper and pedestrians.
For athletes or advanced elevators;
- Enact Dynamic boards (For example, shoulder taps, planks pull) for raised challenge.
- Use Variations for controlled seatshow Swiss ball crunches or Dead errorssparse and strictly.
Example of the main program of the week.
| Day | Exercise | Sets: Duration / Reps: |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Holding a front board | 3 × 30-60 seconds |
| Wednesday | Sideboard (each side) | 3 × 30 seconds |
| Friday | Dead error or controlled sitter | 3 × 10-12 slow, controlled answers |
Conclusion. Which creates a stronger basis.
Both of them Boards and sitters Offer benefits, but they serve for different purposes. For most people, especially in spinal health, posturic resilience or functional movement, boards are superior choiceA number of they build deep main stability, reduce the risk of injury and support sports presentation of different sports and activities.
Sit-Up can still be helpful to target the dynamis of Rectus abdominal, but they should be carefully approached, especially if Lyumbar’s health is worrying. After all, the best Basic courses programs integrate Isometry and dynamic elementsbalancing stability with mobility to build a steady and good round trunk.
Links:
- McGill, SM (2007). Low back disorders. Evidence-based prevention and recovery. Human cinema.
- Ekstrom, Ra, Donatelli, Ra, & Carp, KC (2007). Electrical analysis of the main trunk, hip and muscle analysis during the recovery exercises. J Orthop Sports Phys:37 (12), 754-762.
- Axler, CT, & McGill, SM (1997). Low back loads for a variety of abdominal exercises. Looking for the safest challenge of abdomen. Medicine and science in sports and exercises29 (6), 804-811.
- Willdon, JM (2007). Main stability course. Program programs: Magazine about power and ventilation research21 (3), 979-985.
- Schoenfeld, BJ (2010). Mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application for resistance course. Magazine about power and ventilation research24 (10), 2857-2872.
Source link